GaN Technology Device Chargers: The Future of Efficient Power Delivery
The way we charge our devices has transformed drastically over the last decade. From oversized, slow-charging bricks to sleek, fast, and portable solutions, the evolution has been nothing short of revolutionary. At the heart of this change are GaN technology device chargers, which combine cutting-edge semiconductor advancements with consumer convenience. More than just smaller chargers, GaN technology device chargers represent an entirely new level of efficiency, speed, and sustainability in everyday power delivery.
As the demand for powerful gadgets increases—whether laptops, gaming consoles, or 5G-enabled smartphones—the need for chargers that can keep up is greater than ever. Traditional chargers often fall short, leading to longer charging times, bulkier travel bags, and wasted energy. GaN technology device chargers, however, address these pain points directly by offering compact powerhouses capable of rivaling or even outperforming traditional adapters many times their size.
Beyond convenience, GaN technology device chargers hold significant implications for the broader electronics industry. With tech giants and accessory manufacturers alike adopting this innovation, the momentum suggests that GaN technology device chargers will dominate power electronics in the coming years. Let’s explore this transformative technology in detail and understand why GaN technology device chargers are becoming indispensable for modern users.
Introduction to GaN Technology
Gallium Nitride (GaN) is not a new material. In fact, it has been around since the 1990s and was originally used in specialized industries like LED lighting, high-power lasers, and even satellite components. Its unique semiconductor properties allow for faster electron mobility and higher voltage handling capabilities compared to silicon. These advantages made it perfect for industries where performance and efficiency were critical but cost wasn’t necessarily the deciding factor.
When engineers began integrating GaN into consumer electronics, however, it became clear that this was more than just an incremental improvement. Unlike traditional silicon, GaN allows for smaller transistors that switch faster and generate less heat, creating a ripple effect in both performance and device design. This opened the possibility of developing GaN technology device chargers that were not just compact but also capable of delivering rapid charging speeds across multiple devices simultaneously.
Today, GaN is transitioning from a niche semiconductor to a mainstream powerhouse. By harnessing the unique properties of this material, manufacturers can now create efficient, durable, and portable GaN technology device chargers that better align with the lifestyle of the modern, mobile consumer. The rollout of GaN technology device chargers marks the beginning of a larger semiconductor revolution.
From Silicon to GaN: A Paradigm Shift in Charging
Silicon has dominated the electronics industry for over 50 years. Its abundant availability, relatively low cost, and adequate performance made it the backbone of transistor development and, by extension, all electronic devices. However, as electronic gadgets grew more powerful and demanding, silicon’s limitations became increasingly evident. Size, heat management, and efficiency were constant roadblocks in improving the charging experience for portable devices.
GaN semiconductor material overcomes these barriers with higher switching frequencies and greater power efficiency. This allows components inside the charger—like transformers and inductors—to shrink significantly, giving rise to GaN technology device chargers that are one-third the size of traditional adapters but three times more powerful. A GaN charger that delivers 65W of power is often the same size as a 20W silicon charger, illustrating just how revolutionary this shift has become.
The adoption of GaN technology device chargers represents more than just improved design—it signals a paradigm shift in charging. Where silicon hit its ceiling, GaN technology device chargers open a new frontier that enables fast-charging laptops, powering multiple devices at once, and maintaining extremely portable form factors. It is a direct response to the increasing need for convenience and efficiency in our fast-paced, tech-forward world.

Why GaN Technology Device Chargers Outperform Traditional Chargers
The biggest reason GaN technology device chargers are ahead of their silicon counterparts lies in their efficiency. By conducting electrons faster and with less resistance, GaN avoids the problem of wasted energy that plagued silicon chargers. This results in improved cooling, less heat generation, and safer operating conditions for both the charger and connected devices. For consumers, this translates into longer-lasting hardware and reduced charging times.
Another standout feature of GaN technology device chargers is their portability. Unlike older, brick-sized adapters that were inconvenient to carry around, GaN technology device chargers are lightweight and pocket-sized even at higher wattages. Travelers no longer have to carry a separate charger for their laptops, phones, and tablets. A single GaN technology device charger with multiple ports often supports all these devices, freeing up luggage space and reducing clutter.
Finally, GaN technology device chargers are forward-compatible with the latest charging standards like USB-C PD (Power Delivery). This universal compatibility means that one charger can cover a wide range of devices, from small gadgets like earbuds to power-intensive machines like gaming laptops. The combination of speed, versatility, and compact design makes GaN technology device chargers a clear winner.
How GaN Chargers Work Technically
At the core of GaN technology device chargers are advanced GaN transistors that can switch current at much higher frequencies than their silicon equivalents. This increased switching speed is critical because it allows for the reduction of bulky components within the charger, like coils and capacitors. Smaller components mean smaller chargers, without sacrificing power output. This is why a 100W GaN technology device charger often looks like a tiny cube compared to a silicon-based brick of the same capacity.
The switching efficiency also translates directly into reduced energy loss. Traditional silicon chargers waste more power in the form of heat. With GaN technology device chargers, this inefficiency is minimized significantly. By generating less heat, GaN technology device chargers also lessen the need for additional cooling mechanisms, reducing design complexity and making the overall structure both efficient and durable.
In practice, this means more power is delivered directly to your device’s battery, leading to faster charging cycles. Because GaN technology device chargers can operate safely at higher voltages and currents, they are able to match the power demands of high-performance laptops and smartphones—something silicon-based chargers increasingly struggle to provide.

Real-World Benefits for Consumers
For consumers, the most immediate benefit of adopting GaN technology device chargers is convenience. A single GaN technology device charger often replaces three or more traditional adapters. For instance, a student with a laptop, tablet, and smartphone no longer has to carry multiple cords and bricks in a backpack. Instead, one lightweight multi-port GaN technology device charger can handle it all efficiently.
The second major benefit is speed. Whether you’re powering up a MacBook Pro before a meeting or topping off your smartphone on the go, GaN technology device chargers deliver the juice at lightning-fast speeds. Many modern models can recharge laptops in under two hours and smartphones in under thirty minutes, saving time for people who are always on the move.
Lastly, GaN’s energy efficiency brings both cost-saving and environmental benefits. With lower power wastage, households that use GaN technology device chargers can see small but consistent reductions in electricity bills. On a global scale, this efficiency shift could contribute significantly to reducing carbon emissions related to device charging.
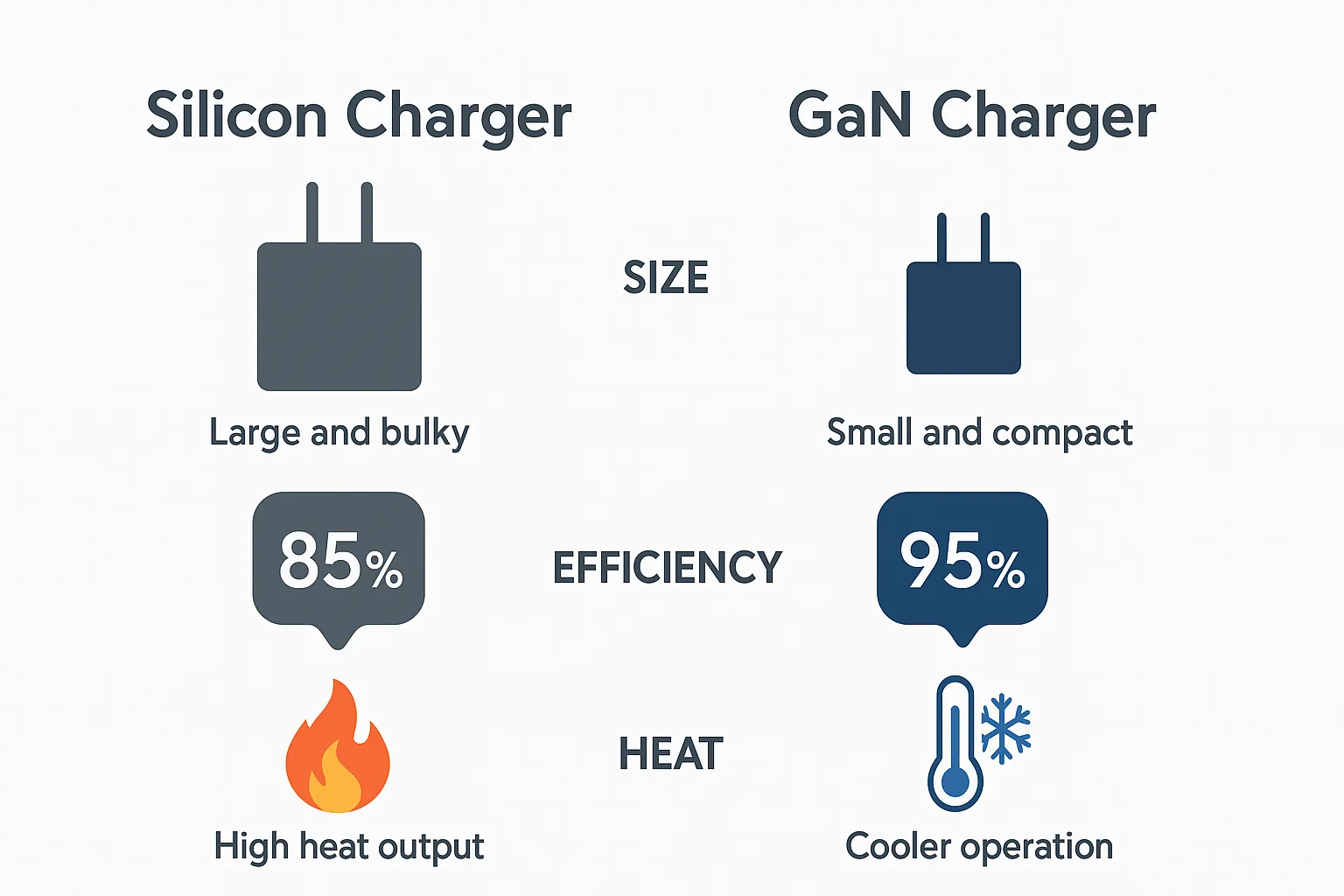
GaN Chargers vs Silicon Chargers: A Comprehensive Comparison
Comparing GaN technology device chargers with traditional silicon chargers highlights why GaN is rapidly gaining traction. Silicon chargers have served consumers well for decades but struggle to meet the demands of modern electronics in terms of power delivery and efficiency. Silicon-based adapters tend to be bulky because they require larger components to handle heat dissipation and voltage regulation. This results in inconvenient, heavy chargers for high-wattage devices like laptops, which can weigh down travelers and desk spaces alike.
In contrast, GaN technology device chargers benefit from the semiconductor’s superior physical characteristics. They operate efficiently at higher switching frequencies, enabling them to shrink the size of internal components without sacrificing power output. This means GaN technology device chargers can provide high wattage outputs—sometimes upwards of 100W—in devices small enough to fit in the palm of your hand. The reduced energy loss in the form of heat not only enhances safety but prolongs the charger’s operational lifetime, making GaN technology device chargers more durable.
Additionally, GaN technology device chargers often embrace cutting-edge charging protocols like USB-C Power Delivery, Quick Charge, and PPS (Programmable Power Supply), allowing them to charge multiple types of devices at optimal speeds. Silicon chargers may support some of these protocols but usually at lower performance levels. Overall, the differences between GaN technology device chargers and silicon chargers are more than incremental; they are transformative, making GaN the go-to technology for future-proof charging solutions.
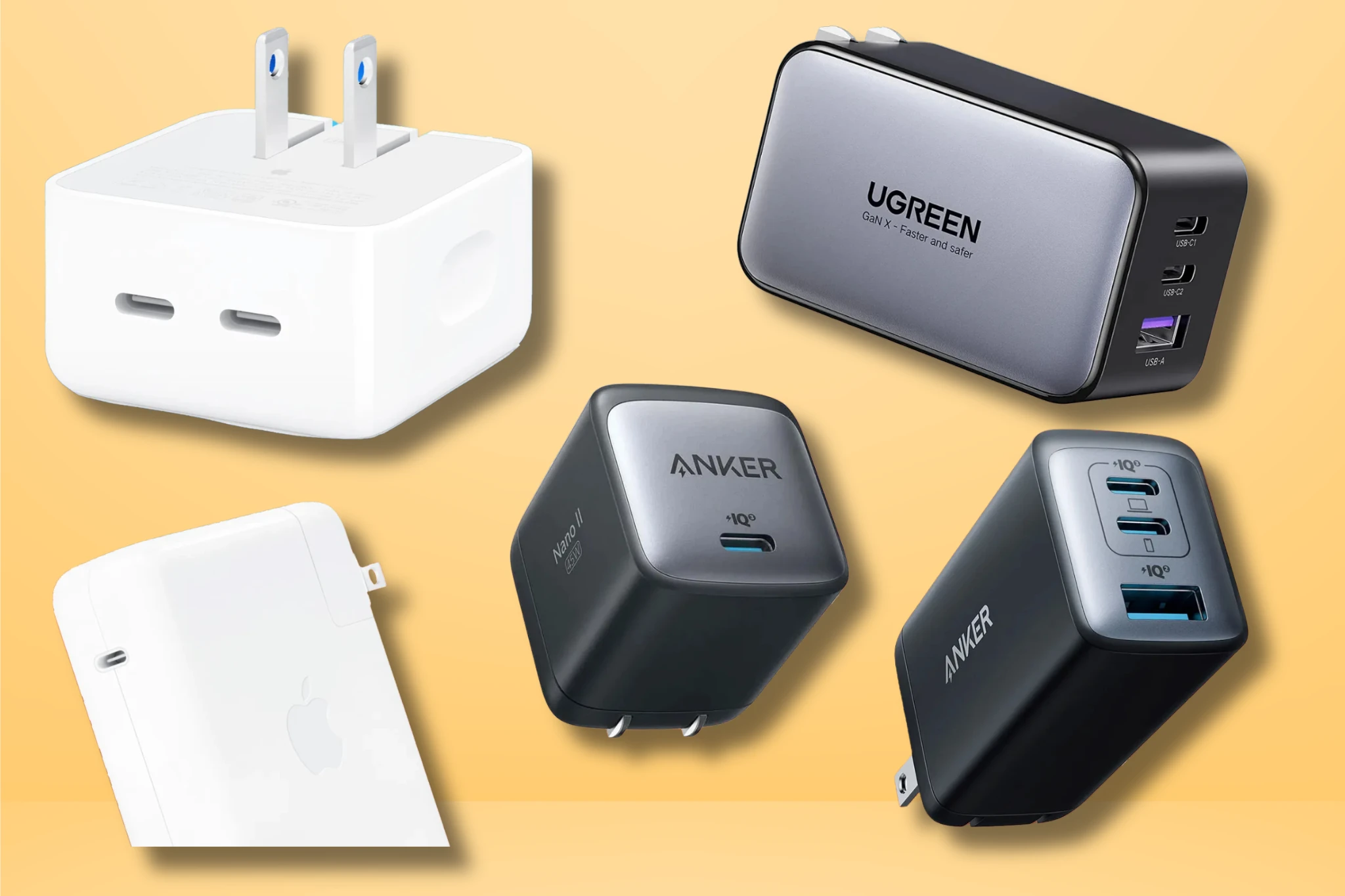

Leading Brands Embracing GaN Chargers in 2025
The rapidly growing market of GaN technology device chargers has attracted numerous brands dedicated to pushing the innovation envelope. Anker, one of the pioneers, continues to dominate with its Nano II and GaNPrime series. Their reputation for quality, safety certifications, and compact design makes them a favorite among tech enthusiasts and everyday users alike. Anker’s chargers often offer multiple ports, enabling simultaneous fast charging of phones, laptops, tablets, and accessories, making them versatile for a wide range of users.
UGREEN is another brand making significant waves with its Nexode line of GaN technology device chargers. Focused on delivering power-hungry outputs in portable formats, UGREEN’s GaN chargers cater especially to professionals and travelers. Their multi-port designs emphasize convenience, allowing users to cut down on the number of chargers they carry. The brand also invests heavily in safety features and built-in protections, making their GaN technology device chargers reliable for long-term use.
Other prominent players include Aukey, Belkin, Apple, and Samsung, each adapting GaN technology to fit their ecosystems and device needs. Apple’s GaN technology device chargers are engineered to complement their iPhones, iPads, and MacBooks, resulting in seamless power delivery and fast charge times. Samsung’s GaN offerings integrate well with the Galaxy ecosystem, offering rapid charging speeds compatible with phones, tablets, and newer laptops. Together, these brands are driving the adoption of GaN technology device chargers into mainstream use.
Image Source: Respective brands

GaN Chargers in Professional and Business Use
Businesses and professionals have greatly benefited from the compactness and efficiency of GaN technology device chargers. Many companies now equip their employees with GaN chargers to reduce weight and clutter during business travel. This switch not only enhances portability but also improves productivity by allowing workers to charge multiple devices quickly and reliably while on the move. GaN chargers’ multi-port designs suit business professionals juggling laptops, smartphones, and wireless headphones.
Moreover, many offices and coworking spaces have integrated GaN technology device chargers into common charging stations, providing flexible and high-speed charging solutions for multiple users. This helps foster a device-friendly environment conducive to long work sessions without power interruptions. Businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact find GaN technology device chargers effective in minimizing energy waste, fitting well with corporate sustainability initiatives.
Furthermore, the durability and enhanced safety features inherent in GaN technology device chargers reduce downtime and costly charger replacements. For companies managing large fleets of devices, this reliability is critical. As remote work continues to rise, GaN technology device chargers allow employees to maintain power at home efficiently without bulk or hassle, supporting seamless work-from-anywhere models.

Environmental Benefits of GaN Technology
As consumers and companies prioritize sustainable living and reduce their carbon footprints, GaN technology emerges as an eco-friendly innovation in the charging arena. GaN technology device chargers are more energy-efficient than silicon chargers, minimizing wasted power as heat and reducing electricity consumption at a global scale. Considering billions of rechargeable devices worldwide, this efficiency translates to significant energy savings and less environmental strain.
Smaller GaN technology device chargers also require fewer raw materials—plastics, metals, and electronic parts—due to their compact designs. This leads to less waste generated during manufacturing, transportation, and disposal. The smaller size also means lighter shipping weights, which helps reduce carbon emissions associated with logistics. By consolidating multiple ports into one device, consumers reduce the need to purchase and dispose of numerous chargers, contributing to less e-waste in landfills.
Additionally, as countries and companies implement stricter regulations on electronic waste and power efficiency, GaN technology device chargers align well with evolving standards. Their durability and energy savings support circular economy models, where devices last longer, consume less energy, and cause less waste. The adoption of GaN technology device chargers worldwide can thus be a meaningful step toward greener tech consumption and production practices.

The Future of GaN Technology Device Chargers
Looking ahead, the prominence of GaN in charging technology is expected to accelerate as devices become more power-hungry and users demand portability. One emerging area is GaN integration into power banks, which will allow ultra-fast, efficient on-the-go charging without bulky or heavy batteries. This will appeal to adventurers, commuters, and professionals who require reliable power far from traditional outlets.
Electric vehicle (EV) chargers are also eyeing GaN technology as a solution to speed up home charging infrastructure. GaN’s ability to handle high voltages efficiently makes it ideal for EV chargers that need to operate safely and quickly within limited space. This could shorten charging times and improve charging station density, helping propel the adoption of EVs worldwide.
Additionally, wireless charging technology is evolving with GaN-enabled pads that offer enhanced efficiency, reduced heat, and faster charging distances. Integration with smart homes and Internet of Things (IoT) devices will create a seamless charging experience where devices recharge unobtrusively throughout the day. As GaN continues to mature, it promises to become the universal standard underlying all forms of power delivery in the near future.

FAQs About GaN Technology Device Chargers
Q1: Are GaN chargers safer than traditional chargers?
Yes. GaN technology device chargers produce less heat due to higher efficiency, reducing the risk of overheating and electrical hazards. Most come with overcurrent, overvoltage, and short circuit protections to keep devices safe during charging.
Q2: Will a GaN charger work with older devices that don’t support USB-C Power Delivery?
Most GaN technology device chargers are backward compatible, featuring USB-A ports and support for common fast-charging protocols, making them versatile for use with older phones and accessories.
Q3: How long do GaN chargers typically last compared to silicon chargers?
GaN technology device chargers generally have a longer lifespan because they run cooler and handle power more efficiently, which reduces internal stress on components over time.
Q4: Are GaN chargers more expensive than their silicon counterparts?
Initially, yes, due to advanced materials and production costs. However, as manufacturing scales, prices have come down significantly, making GaN technology device chargers accessible across many price points.
Q5: Can GaN chargers charge laptops as fast as dedicated laptop chargers?
Depending on wattage, GaN technology device chargers often match or exceed the charging speeds of traditional laptop adapters, especially when equipped with USB Power Delivery and appropriate wattage ratings.

Conclusion
GaN technology device chargers have ushered in a new era of charging that emphasizes speed, efficiency, portability, and environmental responsibility. Their ability to pack high wattage into small, lightweight designs makes them indispensable for modern electronics users ranging from casual smartphone owners to professionals with multiple devices.
With superior heat management, broad device compatibility, and sustainable benefits, GaN technology device chargers do more than just simplify power delivery—they enhance user experience and contribute to global energy savings. As technology evolves and demand for faster, smarter charging grows, GaN technology stands at the forefront of this revolution.
Adopting a GaN technology device charger today means investing in the future of power delivery—where speed, convenience, and sustainability coexist seamlessly. Whether for personal use, business, or travel, GaN technology device chargers are becoming the new gold standard for powering the devices that drive our connected lives.
Follow AI Tech Unboxed for more insights and the latest updates in technology innovations.



